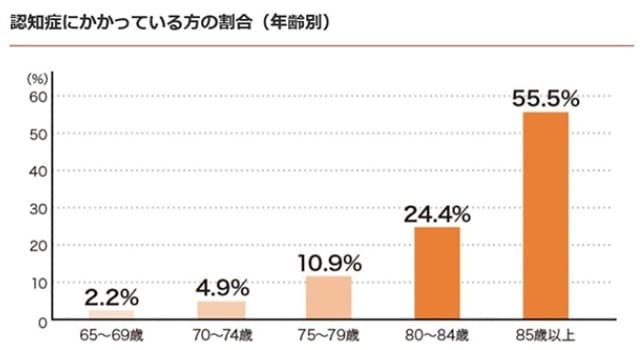
According to the 2012 Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare’s Study on the Future Estimation of the Elderly Population with Dementia in Japan, the prevalence of dementia by gender and age group was found to be increasing, and it is said that more than half of Japan’s population may have dementia.
Dementia is a disease that is said to begin and progress asymptomatically from the mid-40’s to 50’s, which develops fully after 20 to 30 years. Therefore, it is clear that dementia prevention starting from this age group is crucial.
General disease prevention is divided into three stages: primary prevention, secondary prevention and tertiary prevention. “Primary prevention” refers to making changes in lifestyle habits so that individuals do not get sick. “Secondary prevention” refers to the early detection and treatment of illnesses to suppress its progress from becoming more severe. Lastly, “tertiary prevention” refers to the treatment and prevention of its recurrence.
However, unlike other diseases, if dementia is in the “secondary prevention” stage, it is difficult to completely cure it even if the progression can be delayed as there is no treatment as of yet. Therefore, in the case of dementia, “primary prevention” is very important. Individuals in their 40’s and 50’s are in the “primary prevention” phase, so it is important to first prevent high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity, which are factors leading to a high risk of dementia, so let’s try to reduce the risk of dementia by reviewing our lifestyle!
SOURCE: 2012, “Study on the Future Estimation of the Elderly Population with Dementia in Japan”, “Prevalence of Dementia by Age Group”, MHLW Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (MHLW Special Research Project).